LLM Penetration Testing: Securing the Future of AI
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI's GPT, Google's Gemini, Meta’s LLaMA, and DeepSeek, are revolutionizing industries with their ability to generate human-like text, enhance decision-making, and automate complex workflows. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram are also leveraging these AI systems to improve user experiences and business operations. However, as LLMs become more embedded in digital ecosystems, they introduce significant security risks. Cybercriminals are exploiting vulnerabilities such as prompt injections, adversarial attacks, and data poisoning, making AI security a top priority for businesses leveraging these technologies.
LLM Penetration Testing: Elevate Your Cybersecurity with DigiFortex
At DigiFortex, we specialize in LLM penetration testing to identify and mitigate these risks, ensuring the safety and reliability of your AI-driven systems. In this blog, we’ll explore the concept of LLM penetration testing, its importance, and how DigiFortex's structured workflow helps organizations secure their AI ecosystems.
Request free consultation - Click Here
Understanding LLM Penetration Testing
LLM stands for Large Language Model. It’s a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can understand and generate human-like text based on the data it has been trained on. For example, LLMs can perform tasks like writing essays, answering questions, translating languages, or even creating code and users interact with LLMs via a conversational interface, submitting queries or prompts that the model processes and responds to in real-time.They are used in applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, and content creation tools. The most well-known LLMs include models like OpenAI’s GPT.
LLM penetration testing systematically evaluates AI models to identify vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches, unauthorized access, misinformation generation, model manipulation, or prompt-based exploits. This specialized security testing also addresses emerging threats such as LLM jailbreaks, indirect prompt injections, model inversion attacks, and supply chain risks in AI deployments. As LLMs become more integrated into critical systems, proactive security testing is essential to prevent adversarial misuse and ensure robust AI protection.
Key Risk Areas for LLMs
-
User Inputs/Prompts
- Maliciously crafted prompts can manipulate model behavior or extract sensitive information.
- Attackers can bypass content restrictions using indirect or direct prompt injection techniques.
-
Training Data
- Poisoned training data can introduce biases, misinformation, or vulnerabilities.
- Attackers can inject malicious scripts to influence model outputs.
-
APIs and External Plugins
- APIs and plugins interacting with LLMs can be exploited for unauthorized access.
- Attackers can manipulate responses or cause service disruptions.
-
Machine Learning Model
- Sophisticated querying techniques can expose weaknesses in the model’s architecture.
- Reverse engineering attempts can compromise intellectual property and model security.
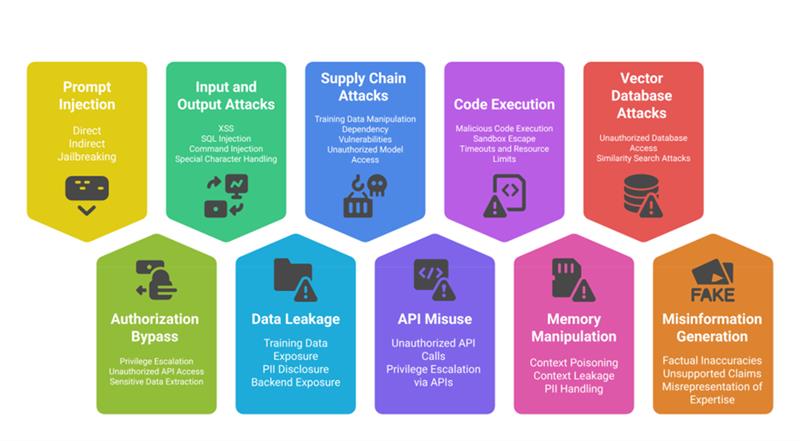
Top Vulnerabilities of LLMs
-
Prompt Injection Attacks
- Direct Prompt Injection: Injecting malicious prompts to bypass or alter system behavior.
- Indirect Prompt Injection: Manipulating external inputs like APIs to change model responses subtly.
- Override System Instructions: Modifying internal instructions, bypassing ethical guardrails.
- Jailbreaking: Circumventing restrictions to force the model into generating unauthorized responses.
-
Authorization Bypass
- Escalation of Privileges: Gaining unauthorized access to restricted data.
- Unauthorized API Access: Executing API calls that expose sensitive functionality.
- Sensitive Data Extraction: Inducing the model to reveal confidential data.
-
Input and Output Attacks
- SQL Injection: Manipulating model-generated queries to exploit databases.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Injecting scripts into LLM responses to execute malicious code.
- Command Injection: Executing unauthorized shell commands through user input.
- Special Character Handling: Exploiting malformed characters to trigger unintended behavior.
- Misinformation Generation: Causing the model to generate incorrect or harmful outputs.
-
Data Leakage
- Training Data Exposure: Extracting data used for training through specific queries.
- Personal Information Disclosure: Forcing the model to reveal user-specific data.
- Backend Exposure: Identifying API keys, system functions, or other technical details.
-
Supply Chain Attacks
- Training Data Manipulation: Poisoning datasets to introduce vulnerabilities.
- Dependency Vulnerabilities: Exploiting weaknesses in external libraries or plugins.
- Unauthorized Model Access: Gaining control over model versioning and deployment.
-
API Misuse
- Privilege Escalation via APIs: Manipulating API parameters to bypass access controls.
- Unauthorized API Calls: Forcing LLM-generated requests to access restricted resources.
-
Code Execution
- Malicious Code Injection: Injecting harmful code that gets executed in the LLM environment.
- Sandbox Escape: Bypassing security measures in code-executing models.
- Timeouts and Resource Limits: Testing if execution restrictions prevent DoS attacks.
-
Memory Manipulation
- Context Poisoning: Altering the model’s memory or context for future interactions.
- Context Leakage: Extracting unintended data from session memory.
- PII Handling: Ensuring the model does not retain or expose sensitive information.
-
Vector Database Attacks
- Unauthorized Database Access: Attempting to retrieve protected vector data.
- Similarity Search Leaks: Exploiting search functions to infer confidential data.
Request free consultation - Click Here
AI/LLM Penetration Testing Approach
-
Reconnaissance:
Gather information on LLM architecture, training sources, APIs, plugins, and data handling. -
Threat Analysis:
Identify vulnerabilities in AI models, data pipelines, and integrations, assessing risks like prompt injection, data poisoning, and model leakage. -
Threat Modeling:
Simulate attack scenarios to assess security gaps. -
Model Theft:
Reverse-engineering or cloning the model to replicate its capabilities. -
Impact Assessment and Reporting:
Document findings, assess risks, and provide actionable recommendations.
Why Is LLM Penetration Testing Essential?
-
Data Security:
LLMs are often trained on vast datasets, which may contain sensitive or proprietary information. Testing ensures this data is not unintentionally exposed. -
Regulatory Compliance:
Industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services require strict adherence to data protection laws like GDPR and HIPAA. LLM penetration testing helps demonstrate compliance. -
Trust and Reputation:
A compromised AI system can erode customer trust and damage an organization’s reputation. Proactive testing mitigates these risks. -
Mitigation of Bias and Misinformation:
Testing ensures LLMs are not susceptible to adversarial attacks that exploit biases or spread misinformation. -
Future-Proofing AI Systems:
By identifying and fixing vulnerabilities today, businesses can ensure their LLMs remain secure against emerging threats.
DigiFortex LLM Penetration Testing (VA/PT) Workflow
At DigiFortex, our structured approach ensures comprehensive testing of your LLM deployments. Here’s how we do it:
-
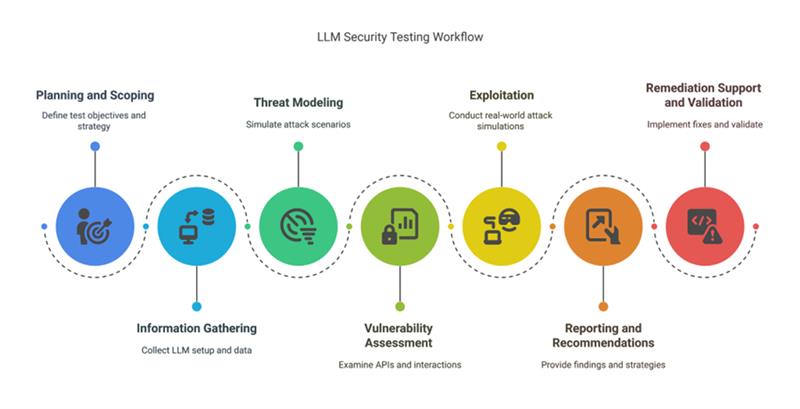
Planning and Scoping:
The process begins by defining the scope and objectives of the test. Critical components, such as APIs, datasets, and integrations, are identified. A strategy is developed to minimize disruption to ongoing operations while ensuring thorough testing. -
Information Gathering:
Detailed information about the LLM is collected, including its setup, training data, configuration, and connections to external systems. This step identifies potential entry points or vulnerabilities in the model and its environment. -
Threat Modeling:
Attack scenarios are created to simulate potential risks. Focus areas include input vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, data exposure, and misuse of the model. This step ensures testing targets areas with the highest potential impact. -
Vulnerability Assessment:
The system is examined for weaknesses. Tests are conducted on APIs, communication channels, and user interactions to detect security gaps, such as data leakage, improper access controls, or prompt injection vulnerabilities. -
Exploitation:
Real-world attack simulations are carried out to assess the actual impact of discovered vulnerabilities. This includes testing for malicious inputs, data theft, or manipulation of the model’s responses to determine the severity of risks. -
Reporting and Recommendations:
A detailed report is prepared, outlining the findings and categorizing risks by their severity. Actionable recommendations are provided to address each vulnerability effectively. -
Remediation Support and Validation:
Support is provided to implement fixes and strengthen system security. Once the remediation is complete, a re-test is conducted to confirm that vulnerabilities have been resolved. A final report is delivered to ensure the system is secure and ready for deployment.
DigiFortex’s workflow ensures that LLM systems are robust, safe, and compliant with security standards, allowing businesses to confidently deploy AI solutions.
Request free consultation - Click Here
Challenges in LLM Penetration Testing
While LLM penetration testing is vital, it also comes with unique challenges:
- Evolving Attack Vectors: New threats like LLM jailbreaks, indirect prompt injections, and model extraction attacks make security testing more complex.
- Limited Transparency: Proprietary LLMs (e.g., GPT, Gemini) restrict access, making in-depth security assessments difficult.
- Data Poisoning & Manipulation: Attackers can inject harmful data to bias or backdoor AI models undetected.
- Ethical & Compliance Concerns: Security testing must balance risk assessments with legal and ethical AI usage guidelines.
- Supply Chain & API Risks: Third-party integrations increase exposure to hidden vulnerabilities and dependencies.
- Dynamic & Contextual Exploits: LLM vulnerabilities often depend on input context, making them harder to detect and replicate.
DigiFortex overcomes these challenges with expertise in AI security and a tailored approach to each client’s unique requirements.
Why Choose DigiFortex for LLM Penetration Testing?
At DigiFortex, we understand the unique challenges of securing LLMs and other AI systems. Here’s why businesses trust us:
- Certified Experts: CIPPE, CCSA, CCNA, HPOV, DCPLA, CEH, CISSP, CISM, ISO27001 LA.
- ISO 27001:2022 certified and CERT-In empanelled: DigiFortex is ISO 27001:2022 certified and CERT-In empanelled for providing Information security services. We bring unparalleled expertise to every project.
- Specialized Expertise: Our team combines deep knowledge of AI systems with advanced cybersecurity skills.
- Tailored Approach: We customize our testing methodologies to your specific LLM deployment.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Our reports include clear insights and actionable recommendations.
- Proven Track Record: We’ve successfully secured AI systems across industries, from healthcare to finance.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to embrace AI-powered solutions, securing Large Language Models is more critical than ever. LLM penetration testing is an essential step in protecting your AI systems, ensuring they deliver value without compromising security or compliance.
At DigiFortex, we’re committed to helping organizations harness the power of AI securely. With our expertise in LLM penetration testing, you can stay ahead of emerging threats and build trust in your AI-driven solutions.
Ready to secure your LLM systems? Contact Digifortex today! to learn more about our AI security services.